About Me
I'm currently a PhD student at The University of Sheffield, working as part of the Visual Computing Research Group. My research interests lie in Computer Graphics, mainly on the physically-based animation of deformable objects and fluids. I am currently working on multiphysics simulations of interactions between deformable objects and liquids.
Research
This page contains published research, video demonstrations and links to any published code.
______________________________________________________________________________________________
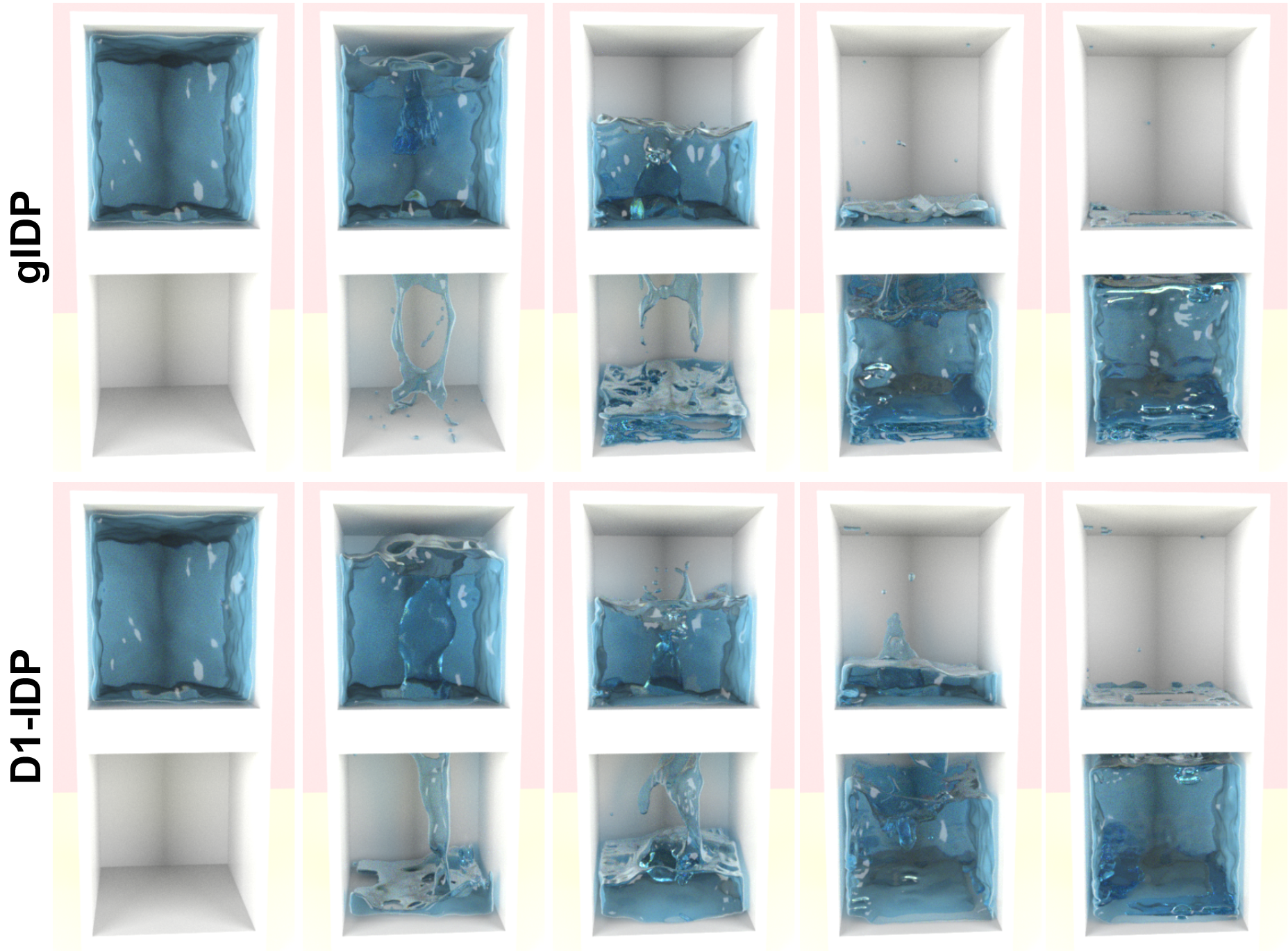
Extending Implicit Density Projection for Multiphase Fluids
Authors: Robert Dennison, Steve Maddock
The work was accepted as a paper for Computer Graphics International 2025 in Hong Kong, and was presented by myself.
Abstract
To increase the realism of fluid simulations, interactions between different fluids (such as water and air, or water and oil) must be considered.
This allows for the simulation of phenomena such as the ‘glugging’ effect seen when a filled bottle is turned upside-down and air must fill the space left by the liquid.
A common approach to fluid animation is to use Particle-in-Cell (PIC) methods.
However, such methods are known to lose fluid volume over time due to accumulating numerical errors, an issue that is exacerbated when simulating multiple interacting fluids.
Implicit Density Projection (IDP) is used to overcome volume preservation issues for PIC methods.
However, it is formulated for single fluids.
To address this, we present two novel extensions to IDP: generalised IDP and D1-IDP.
Generalised IDP extends IDP to multiple fluids.
D1-IDP then further improves on the volume preservation capabilities.
We show that D1-IDP is particularly good in multiphase fluid simulations with complex fluid interfaces.
We also demonstrate its applicability to multiphase simulations involving variable density fluids.
D1-IDP is able to achieve a maximum volume error of < 1.0% for the majority of presented scenarios, while having a negligible impact on computation performance compared to generalised IDP.
The paper has not yet been published, but will be available in the Conference Proceedings when released.
The code repository for this work will be made available upon publication of the paper.
Demonstration Videos
The supplementary video showcasing the demonstrations in the paper. Rendered using Houndini.
______________________________________________________________________________________________
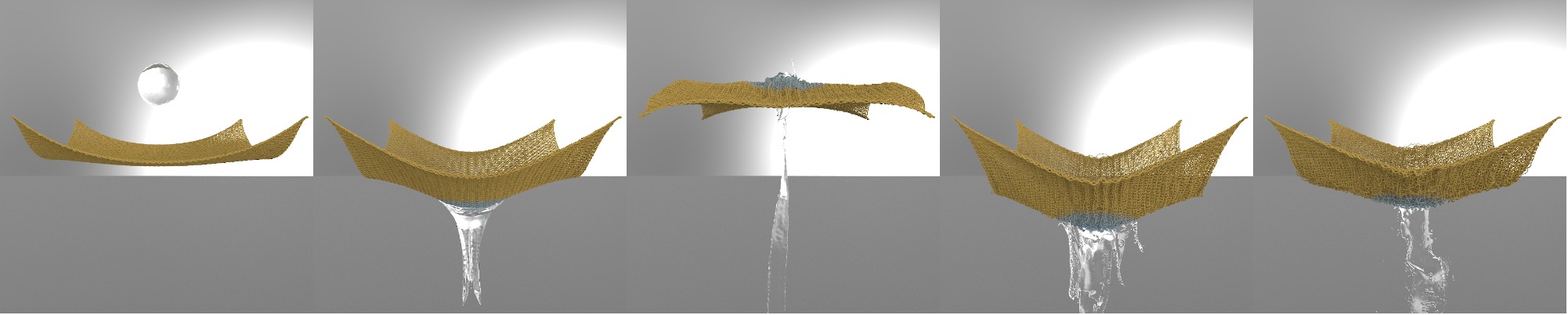
Using The Polynomial Particle-In-Cell Method For Liquid-Fabric Interaction
Authors: Robert Dennison, Steve Maddock
The work was accepted as a short paper for GRAPP 2024, and was presented by myself.
Abstract
Liquid-fabric interaction simulations using particle-in-cell (PIC) based models have been used to simulate a wide variety of phenomena and yield impressive visual results.
However, these models suffer from numerical damping due to the data interpolation between the particles and grid.
Our paper addresses this by using the polynomial PIC (PolyPIC) model instead of the affine PIC (APIC) model that is used in current state-of-the-art wet cloth models.
The affine transfers of the APIC model are replaced by the higher order polynomials of PolyPIC, thus reducing numerical dissipation and improving resolution of vorticial details.
This improved energy preservation enables more dynamic simulations to be generated although this is at an increased computational cost.
The published paper can be found here.
The code repository for this work can be found here.
Demonstration Videos
A rendered view of a ball of fluid falling onto yarn-based fabric. Rendered using Houndini.
Comparisons of simulations using APIC and PolyPIC.
Video Games
After graduating I spent 2 years working for Sumo Warrington and was able to work on some really exciting projects!
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Mortal Kombat 1

Contributions:
- Extending Unreal Engines animation tool Sequencer to give additional animation controls to artists.
- Working with Havok Cloth physics - this was my first foray into physics-based animation.
- Working with Unreals skeletal mesh system to fix ragdoll issues.
Released on 19th Sep 2023 on various platforms: Windows, PlayStation 5, Xbox Series X/S, Nintendo Switch.
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Football Manager 2021

Contributions:
- Integrating libvpx video codec for exporting match highlights.
- Fixing Xbox UI bugs.
Released between 24th Nov 2020 - 15th Dec 2020 on various platforms: Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, Xbox One, Xbox Series X/S, Nintendo Switch.
Blog
This page contains other projects that aren't published research.
Houdini - 1. MPM
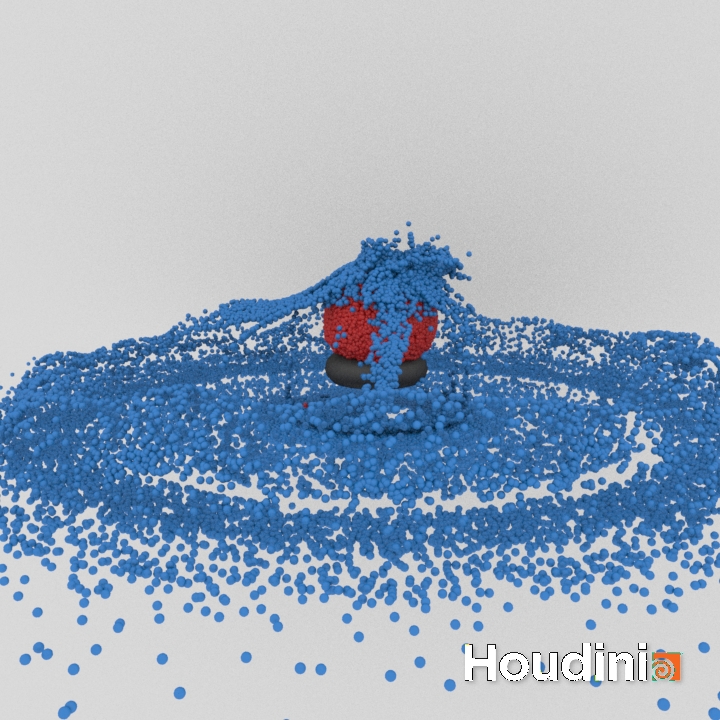
I've been using Houdini to produce the renderings of simulation output during my PhD, so I thought I would spend some time learning about using it. Today I have looked into MPM simulations, and followed the intro part of the MPM Houdini Masterclass.
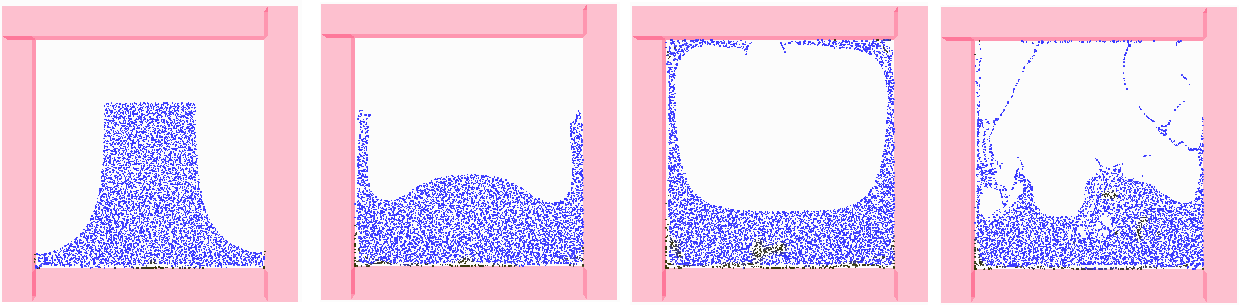
Multiphase PIC Fluids
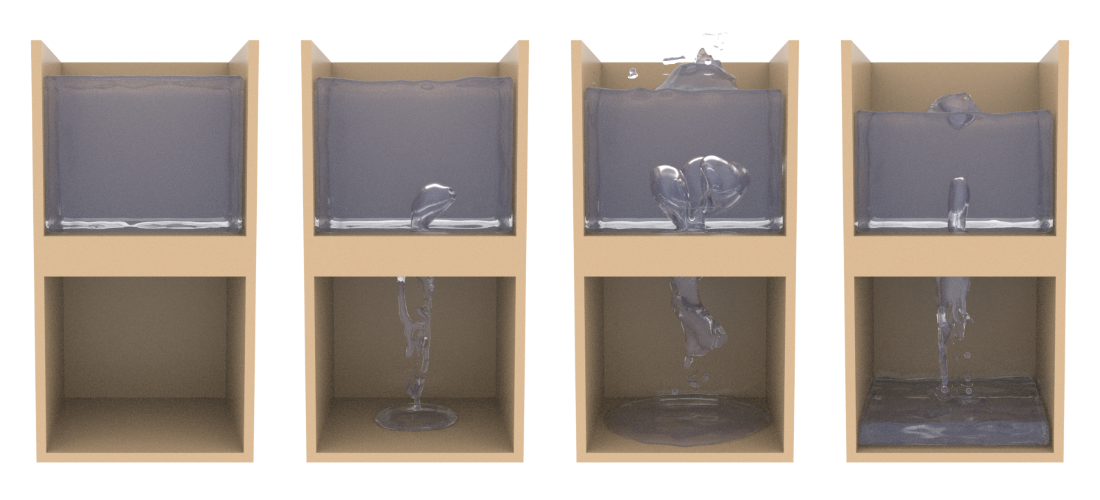

A multiphase fluid simulation using the affine particle-in-cell method (APIC), based on the MultiFLIP paper by Boyd and Bridson (link to paper here).
PIC Fluids
Fluid simulation using the particle in cell method. Implemented in C++ on the CPU, making use of oneTBB for multithreading.